Table Of Contents
- A Year-End Lease Administration Audit involves reviewing lease agreements at the year's end.
- What steps should be taken to prepare lease administration documents consistently throughout the year?
- Year-end disclosure reports
- Following the audit: creating a budget and preparing for the upcoming period.
- Conclusion
ClicLease provides services to large enterprises worldwide, and we have seen the difficulties companies face at the close of each fiscal year. The lease accounting year-end audit is a complicated and often lengthy process. Nonetheless, it is essential for achieving accurate financial reporting and meeting regulatory obligations, as well as for enhancing cost efficiency within the enterprise. To assist in making this process more manageable, we have created this guide on year-end audits, where we share our insights and best practices that we have gathered, especially in light of the recent lease accounting changes. In this guide, you will learn:
- A Comprehensive Overview of Year-End Lease Administration Audits and the Challenges Faced by Businesses.
- Strategies for Maintaining Lease Administration Records Throughout the Year.
- Best Practices for Streamlining the Year-End Audit Process.
- Post-audit budgeting and planning.
This guide was developed by a group of ClicLease specialists who have collaborated closely and reviewed best practices according to IASB and Big4 audit firms. Some companie frequently manage over 1000 lease agreements, and our experts support them in establishing effective lease management practices and ensuring compliance with regulations.
1.An overview of what a Year-End Lease Administration Audit entails, its significance, and the difficulties associated with it.
What is the audit conducted at the end of the year for lease accounting?
A financial audit involves an impartial external review of an organization's financial documentation, transactions, and processes conducted by qualified third-party auditors. During a year-end audit, auditors assess the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of lease accounting information by reviewing specific financial documents and records, such as lease agreements and schedules. Although lease accounting standards have existed for some time, numerous companies still encounter difficulties in keeping accurate records and adhering to accounting regulations.
What makes the year-end lease administration audit so crucial?
The year-end lease administration audit is an essential process that needs to be performed with precision. This audit offers companies a chance to:
Review Record
Examine their lease accounting records, spot any mistakes or missing information, and make necessary corrections prior to the conclusion of the financial year.
Compliance
Make sure to adhere to accounting standards like IFRS 16, ASC 842, and GASB 87, which mandate that lease liabilities and assets must be recorded on the balance sheet.
Financial Position
Gain a clear understanding of the company's financial status to aid in budget planning and cost optimization for the next fiscal year.
Challenges for enterprises
Lease accounting can be a complicated and demanding task, particularly during year-end audits. It requires the tracking and management of lease agreements, calculating payment amounts, and ensuring adherence to accounting regulations. This process can become more intricate for companies that have extensive lease portfolios or operate across various jurisdictions, currencies, and languages. Let's explore the reasons why year-end audits can pose challenges for businesses:
- A high volume of leases: Numerous companies possess multiple leases that must be recorded, complicating and prolonging the year-end audit process.
- Complexity of lease terms: Leases often include complex terms and conditions that must be properly understood and accounted for. This complexity can result in mistakes and inaccuracies in lease accounting, particularly when calculations are performed manually.
- Lack of standardization: The lack of a uniform method for lease administration and accounting can pose difficulties for businesses in maintaining consistency and precision in their accounting procedures.
- Modifications in accounting regulations:Accounting standards continue to develop and have experienced major updates in the last five years. Disclosure requirements can become quite complex, particularly for organizations that must produce reports under both ASC-842 and IFRS-16, mainly due to the differences between the two standards.
Below are the required disclosures for Lease Accounting as outlined by the Accounting Standard.
ClicLease: Required disclosures under IFRS 16 and US GAAP ASC-842
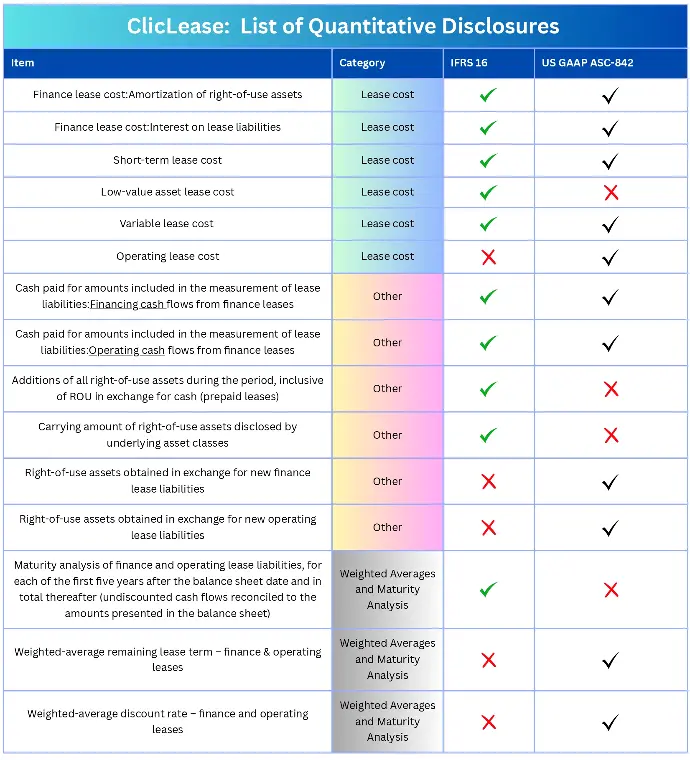
- Limited resources: Numerous businesses face constraints in both resources and expertise regarding lease accounting, making it challenging to efficiently handle the year-end audit process.
- Technology limitations: Certain businesses might lack the technological infrastructure or tools required for efficient lease accounting, which can complicate the year-end audit process even more. Relying on spreadsheets or outdated tools, making changes without a centralized data source, and having multiple data origins can make the year-end audit cumbersome.
- Challenges in detailing and addressing complicated situations.Lease agreements can become quite complicated, particularly when they are long-term and their terms and conditions have evolved over time.
By tackling these issues in advance and utilizing the appropriate tools and expertise, companies can simplify the year-end audit process and maintain precise and compliant lease accounting. In the following section, we will examine the best practices for preparing for the year-end audit throughout the year.
2. What steps should be taken to create lease administration documents over the course of the year?
Five guidelines for conducting calculations throughout the year
Throughout the year, it's important to maintain comprehensive records of all lease agreements and any changes to them, and to frequently check the lease information for accuracy. Here are five guidelines to help facilitate a smoother year-end audit:
- Establish a single centralized repository for all detailed records and lease information. Relying on multiple, unsynchronized data sources can result in various data versions, heightening the likelihood of mistakes. Additionally, your team will spend more time searching for and confirming lease information to locate the accurate version.
- Begin adjusting the closing process by completing tasks earlier in the month for month-end closures, and earlier in the year for preliminary disclosure reporting and year-end audits. This approach will help make the closing process more consistent and ongoing.
- Verify important lease transactions and balances across different reports in the subledger and ensure they match with the consolidated reporting systems.
- Swap out labor-intensive tasks that depend on checklists for streamlined workflow processes that connect various systems.
- Ensure effective communication with all parties involved in the lease, such as leaseholders, accounting teams, and auditors. The organization should establish lease accounting policies and procedures with input from all stakeholders engaged throughout the leasing process. These policies should be clearly documented and shared with the lease accounting team to guarantee that the established processes are applied consistently.
Manual calculations: factors to take into account
Carrying out these intricate calculations in Excel or any other manual tool is a significant undertaking. If you’re calculating your lease data by hand, it's important to have a consistent format across your team, routinely review and refresh the calculations, and maintain comprehensive records of all computations, including any assumptions or estimates involved. Here’s what you need to do:
- Identify all Leases: The initial step in getting ready for a year-end audit in accordance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842 is to recognize all types of leases, which encompass operating leases, finance leases, and short-term leases.
- Determine the Lease Term: According to IFRS 16 and ASC 842, the lease term encompasses any options to extend or terminate the leases that are likely to be exercised. It's important to examine your lease agreements to establish the lease term.
- Determine the obligation related to the lease.The lease liability represents the total value of lease payments throughout the lease duration. This calculation takes into account the minimum lease payments as well as any incentives associated with the lease.
- Determine the Right-of-Use Asset:The right-of-use asset (ROU asset) is calculated by adding the initial value of the lease liability to any lease payments made prior to the start date, any lease incentives obtained, and any direct costs related to the lease.
- Document the lease on your balance sheet.After finishing the calculations for the lease liability and right-of-use asset, you can enter the lease into your balance sheet.
Keep in mind that manually calculating these inputs can lead to human errors and be quite time-intensive. It's important to have all your lease-related information stored in a centralized location, which should include exchange rates, incremental borrowing rates, contract details, termination options, extension clauses, and other essential data. Considering the accounting requirements of IFRS 16 and ASC 842, as well as the substantial amount of data involved for large companies, your accounting team might get overwhelmed with manual calculations while preparing for the year-end audit. Therefore, large enterprises with extensive lease portfolios can only meet the new standards if they utilize sophisticated enterprise-level lease accounting software that features advanced automation.